Supongo que a estas alturas, la mayoría saben que Mac OSX es un sistema operativo cuyo interface gráfico se ejecuta sobre una versión de UNIX.

Para que lo entiendan, es como las versiones antiguas de Windows, que se ejecutaban sobre MS-DOS. Es decir, tenemos una parte básica del sistema operativo que se encarga de las operaciones a bajo nivel y una capa gráfica basada en ventanas que es mucho más amigable para el usuario.
Esto es una herencia de cuando Apple compró NeXT (la empresa que creó Jobs al ser expulsado de Apple) y que propició el regreso de Steve a la marca de la manzana. En ese momento se decidió que NextStep, el sistema operativo de NeXT basado en el kernel Mach y BSD fuera a su vez la base sobre la que desarrollar el sistema operativo de nuestros Macs actuales.
Queda fuera del objetivo de este post (y de mis conocimientos ) explicar mucho más de sistemas operativos, pero creía necesaria la introducción para comprender lo que viene a continuación.
Muchos de nosotros empezamos manejando ordenadores a base de teclear distintos valores en determinadas direcciones de memoria (como el Commodore 64), mientras que otros han “nacido” manejando un ordenador basado en ventanas.
Seguro que unos y otros han leído artículos que hablan de introducir tal o cual comando en la Terminal de Mac OSX. Los más valientes incluso habrán copiado la linea incomprensible de caracteres y pulsado Enter con un cierto miedo a ver qué pasaba…
Así que he pensado que no estaría mal escribir un pequeño artículo para explicar qué es la Terminal y algunos comandos básicos para que el menos puedan ver como funciona y que hay otra forma de manejar vuestros Macs. No sé yo si les será útil en algún momento, pero el saber no ocupa lugar
La Terminal
Antiguamente (vamos, hace más de 25 años) no había entornos gráficos en los ordenadores domésticos (Mac OS nació en 1984 y Windows 1.0 data de 1985), así que los ordenadores se manejaban a través del teclado y había que recordar multitud de comandos, cada uno con una función específica y un montón de modificadores que permitían especificar acciones determinadas de un comando. Así, para ver los ficheros que contenía un disco, en MS-DOS debíamos escribir DIR y pulsar Enter.
Prehistórico verdad, ¿verdad?
Pues la Terminal de nuestros Macs no es más que eso: un vestigio del pasado. Una forma de ejecutar comandos en nuestro Mac a base de escribir instrucciones que el sistema operativo interpreta y ejecuta.
En el caso de Mac OSX, abrir la Terminal significa lidiar con UNIX y conocer sus comandos específicos, de los que veremos algunos más adelante.
Como somos unos valientes, ejecutemos Terminal. Está en Aplicaciones/Utilidades o lo puedes buscar en Spotlight.
Nos aparecerá una pequeña ventana como esta:
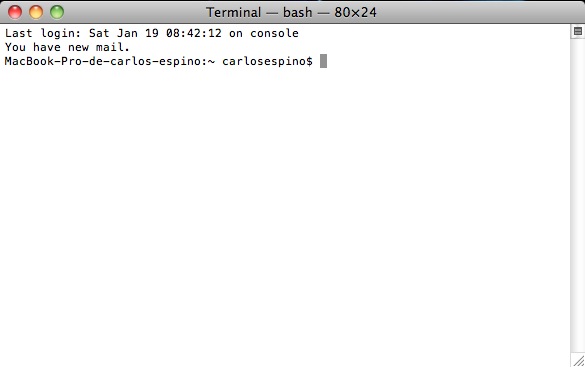
El texto “MacBook-Pro-de-carlos-espino:~ carlosespino$” nos indica que estamos en un ordenador que se llama MacBook-Pro-de-carlos-espino y que nuestro nombre de usuario en dicho ordenador es carlosespino. El símbolo ‘$‘ es sólo el indicador de que está esperando que tecleemos un comando. Para los que vengan de MS-DOS, es lo mismo que el C:\>
Antes de explicar ningún comando, les diré cómo salir de la Terminal: teclea exit, pulsa Enter y cierra la ventana.
Ahora, veamos algunos comandos:
clear (limpiar ventana)
Aunque no es el más importante, he decidido que sea el primero porque cuando usemos otros comandos, la ventana se llenará de texto y lo hará más complicado. Basta teclear clear y pulsar Enter para que se borre todo.
ls (mostrar archivos)
El equivalente del DIR en MS-DOS. Nos muestra todos los archivos que hay en el directorio actual. Y cuando digo archivos, también incluyo directorios. Veamos un ejemplo:

En la captura anterior, me está mostrando los archivos que tengo en mi Mac. Si se fijan, son los mismos que aparecen en el Finder. Lo malo es que así no diferenciamos cuáles son ficheros normales y cuáles directorios, así que mejor usar una opción del comando ls:
ls -l (mostrar archivos en formato largo)
Teclea ls -l y pulsa Intro. Verás que aparece los siguiente:
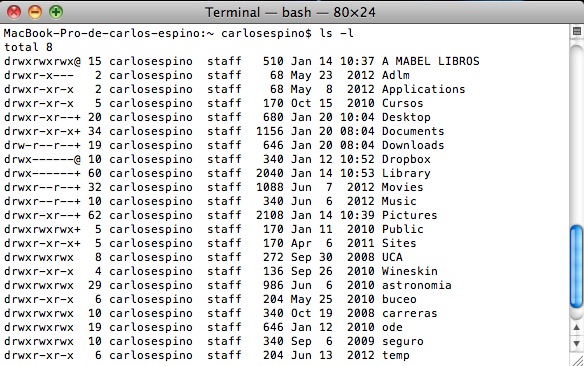
Eso de drwxr-xr-x nos debe sonar a ‘chino’, pero es fácil. La d al principio indica que es un directorio. Si es un fichero, en ese lugar aparecería un guión -.
Los siguientes caracteres son los permisos de dicho archivo. Están en grupos de 3: rwx r-x r-x y son respectivamente, los permisos que tiene el dueño sobre ese archivo, los permisos del grupo y los del resto de usuarios. r significa que se puede leer (read), w que se puede escribir o modificar (write) y x que se puede executar (eXecute).
Así que cuando hablamos de “reparar permisos” con utilidad de disco, nos referimos a estos permisos, ya que por distintas causas (como al instalar un programa nuevo), se pueden modificar y provocar fallos.
El siguiente número indica el número de directorios contenidos en el directorio, luego nos indica quién es el dueño del archivo y a qué grupo pertenece ( staff) el número de bloques que ocupa el archivo, la fecha y por último, el nombre del fichero o directorio.
Aún así, con ls -l no podemos ver todos los ficheros que hay en el directorio, porque no muestra los ocultos. Para ello debemos usar:
ls -la (mostrar todos los ficheros en formato largo)
y nos aparecerá lo siguiente:
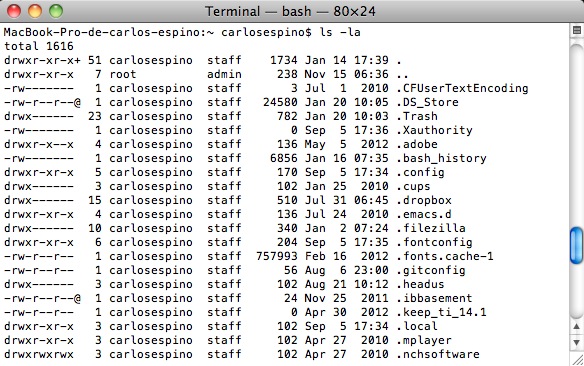
Como pueden observar, los archivos que habitualmente están ocultos son los que empiezan con un punto.
Ahora veamos cómo movernos por los directorios.
cd nombrededirectorio (cambiar de directorio)
Elegi uno de los directorios, por ejemplo Library y escribe cd Library (ojo, que hay que respetar mayúsculas/minúculas). Verás que el prompt del sistema nos muestra en el directorio en el que estamos:
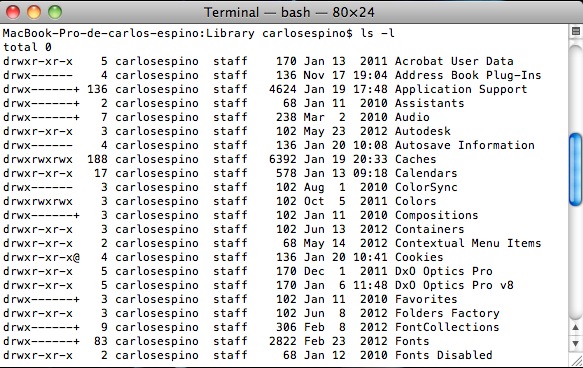
Ahora puedes introducir ls -l para ver los archivos que hay en ese directorio. Para “subir” un nivel e ir al directorio anterior, basta con que teclees cd ..
Ahora que ya sabes moverte por los directorios y ver los archivos que contienen, veamos otros comandos:
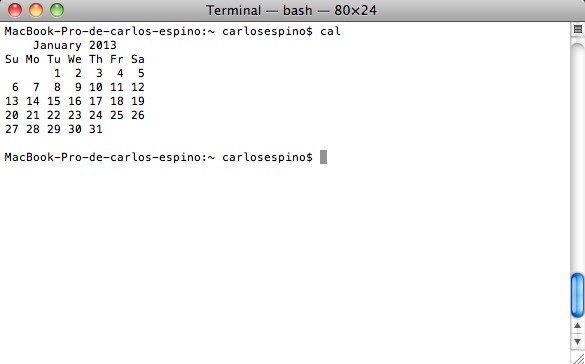
cal (calendario)
Muestra el calendario del mes en curso
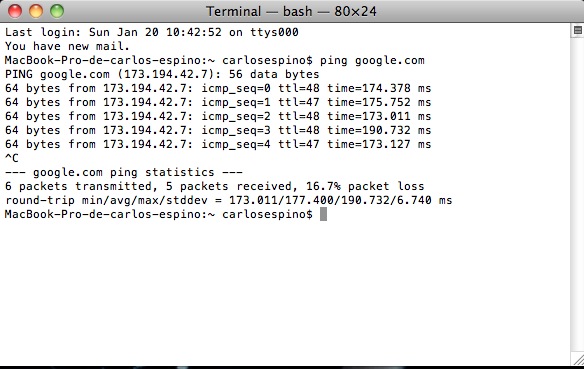
Ping direcciónIP (hacer un ping a una IP)
Quizá alguna vez hayas tenido que hacer un ping a una IP para ver si un servidor estaba respondiendo. En UNIX es tan fácil como teclear ping, seguido de la dirección IP a comprobar:
Pulsa Ctrl-C para dejar de hacer ping y volver al prompt del sistema
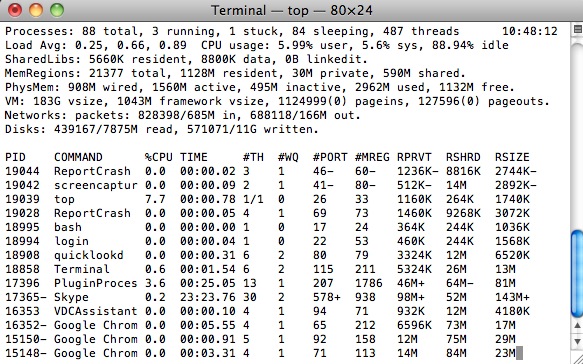
top
Muestra información sobre los procesos que se están ejecutando en nuestro Mac, así como información sobre la memoria, discos, red, etc. (pulsa q para salir)
Hay cientos de comandos y no los podemos explicar todos aquí. Os dejo al final del artículo una serie de enlaces de referencia para que sigáis profundizando. Recordad que desde la línea de comandos se puede hacer de todo, incluido borrar ficheros y cargarte por completo tu disco duro, así que tened cuidad. Por si acaso, si tienes alguna duda con el formato o qué hace algún comando, siempre puedes usar:
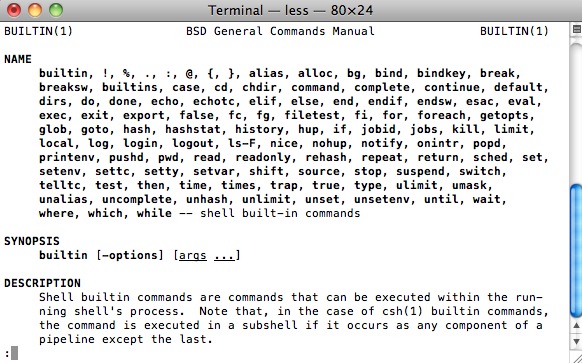
man command (manual)
Que te mostrará el manual con la descripción y opciones que permite el comando que hayas especificado:
Otros sitios donde encontrar más información de sobre la terminal y comandos UNIX:
Finalmente……
Les dejo la lista completa de comandos que pueden realizarse con los link donde se explica que hace cada uno de ellos
An A-Z Index of the Apple OS X command line
alias Create an
alloc List used and free memory
apropos Search the whatis database for strings
awk Find and Replace text within file(s)
b
basename Convert a full pathname to just a filename
bash Bourne-Again SHell
bg Send to background •
bind Display readline key and function bindings •
bless Set volume bootability and startup disk options.
break Exit from a For, While, Until or Select loop •
builtin Execute a shell builtin •
bzip2 Compress or decompress files
c
cal Display a calendar
calendar Reminder Service
caller Return the context of a subroutine call •
case Conditionally perform a command •
cat Concatenate and print (display) the content of files
cd Change Directory •
chflags Change a file or folder’s flags
chgrp Change group ownership
chmod Change access permissions
chown Change file owner and group
chroot Run a command with a different root directory
cksum Print CRC checksum and byte counts
clear Clear terminal screen
cmp Compare two files
comm Compare two sorted files line by line
command Run a command (not a function) •
complete Edit a command completion [word/pattern/list] •
continue Resume the next iteration of a loop •
cp Copy one or more files to another location
cron Daemon to execute scheduled commands
crontab Schedule a command to run at a later date/time
csplit Split a file into context-determined pieces
curl Transfer data from or to a server
cut Divide a file into several parts
d
date Display or change the date & time
dc Desk Calculator
dd Data Dump – Convert and copy a file
declare Declare variable & set attributes •
defaults Set preferences, show hidden files
df Display free disk space
diff Display the differences between two files
diff3 Show differences among three files
dig DNS lookup
dirname Convert a full pathname to just a path
dirs Display list of remembered directories •
diskutil Disk utilities – Format, Verify, Repair
disown Unbind a job from the current login session •
ditto Copy files and folders
dot_clean Remove dot-underscore files
drutil Interact with CD/DVD burners
dscacheutil Query or flush the Directory Service/DNS cache
dseditgroup Edit, create, manipulate, or delete groups
dsenableroot Enable root access
dsmemberutil View user and groups rights
dscl Directory Service command line utility
du Estimate file space usage
e
echo Display message on screen •
ed A line-oriented text editor (edlin)
enable Enable and disable builtin shell commands •
env List or Set environment variables
eval Evaluate several commands/arguments •
exec Execute a command •
exit Exit the shell •
expand Convert tabs to spaces
expect Programmed dialogue with interactive programs
Also see AppleScript
export Set an environment variable •
expr Evaluate expressions
f
false Do nothing, unsuccessfully
fc Fix command (history)
fdisk Partition table manipulator for Darwin UFS/HFS/DOS
fg Send job to foreground •
file Determine file type
find Search for files that meet a desired criteria
fmt Reformat paragraph text
fold Wrap text to fit a specified width
for Loop command •
fsck Filesystem consistency check and repair
fsaclctl Filesystem enable/disable ACL support
fs_usage Filesystem usage (process/pathname)
ftp Internet file transfer program
g
GetFileInfo Get attributes of HFS+ files
getopt Parse positional parameters
getopts Parse positional parameters •
goto Jump to label and continue execution
grep Search file(s) for lines that match a given pattern
groups Print group names a user is in
gzip Compress or decompress files
h
halt Stop and restart the operating system
hash Refresh the cached/remembered location of commands •
head Display the first lines of a file
hdiutil Manipulate iso disk images
history Command History •
hostname Print or set system name
i
iconv Convert the character set of a file
id Print user and group names/id’s
if Conditionally perform a command •
alloc List used and free memory
apropos Search the whatis database for strings
awk Find and Replace text within file(s)
b
basename Convert a full pathname to just a filename
bash Bourne-Again SHell
bg Send to background •
bind Display readline key and function bindings •
bless Set volume bootability and startup disk options.
break Exit from a For, While, Until or Select loop •
builtin Execute a shell builtin •
bzip2 Compress or decompress files
c
cal Display a calendar
calendar Reminder Service
caller Return the context of a subroutine call •
case Conditionally perform a command •
cat Concatenate and print (display) the content of files
cd Change Directory •
chflags Change a file or folder’s flags
chgrp Change group ownership
chmod Change access permissions
chown Change file owner and group
chroot Run a command with a different root directory
cksum Print CRC checksum and byte counts
clear Clear terminal screen
cmp Compare two files
comm Compare two sorted files line by line
command Run a command (not a function) •
complete Edit a command completion [word/pattern/list] •
continue Resume the next iteration of a loop •
cp Copy one or more files to another location
cron Daemon to execute scheduled commands
crontab Schedule a command to run at a later date/time
csplit Split a file into context-determined pieces
curl Transfer data from or to a server
cut Divide a file into several parts
d
date Display or change the date & time
dc Desk Calculator
dd Data Dump – Convert and copy a file
declare Declare variable & set attributes •
defaults Set preferences, show hidden files
df Display free disk space
diff Display the differences between two files
diff3 Show differences among three files
dig DNS lookup
dirname Convert a full pathname to just a path
dirs Display list of remembered directories •
diskutil Disk utilities – Format, Verify, Repair
disown Unbind a job from the current login session •
ditto Copy files and folders
dot_clean Remove dot-underscore files
drutil Interact with CD/DVD burners
dscacheutil Query or flush the Directory Service/DNS cache
dseditgroup Edit, create, manipulate, or delete groups
dsenableroot Enable root access
dsmemberutil View user and groups rights
dscl Directory Service command line utility
du Estimate file space usage
e
echo Display message on screen •
ed A line-oriented text editor (edlin)
enable Enable and disable builtin shell commands •
env List or Set environment variables
eval Evaluate several commands/arguments •
exec Execute a command •
exit Exit the shell •
expand Convert tabs to spaces
expect Programmed dialogue with interactive programs
Also see AppleScript
export Set an environment variable •
expr Evaluate expressions
f
false Do nothing, unsuccessfully
fc Fix command (history)
fdisk Partition table manipulator for Darwin UFS/HFS/DOS
fg Send job to foreground •
file Determine file type
find Search for files that meet a desired criteria
fmt Reformat paragraph text
fold Wrap text to fit a specified width
for Loop command •
fsck Filesystem consistency check and repair
fsaclctl Filesystem enable/disable ACL support
fs_usage Filesystem usage (process/pathname)
ftp Internet file transfer program
g
GetFileInfo Get attributes of HFS+ files
getopt Parse positional parameters
getopts Parse positional parameters •
goto Jump to label and continue execution
grep Search file(s) for lines that match a given pattern
groups Print group names a user is in
gzip Compress or decompress files
h
halt Stop and restart the operating system
hash Refresh the cached/remembered location of commands •
head Display the first lines of a file
hdiutil Manipulate iso disk images
history Command History •
hostname Print or set system name
i
iconv Convert the character set of a file
id Print user and group names/id’s
if Conditionally perform a command •
ifconfig Configure network interface parameters
ipconfig View and control IP configuration state
info Help info
install Copy files and set attributes
j
jobs List active jobs •
join Join lines on a common field
k
kextfind List kernel extensions
kickstart Configure Apple Remote Desktop
kill Stop a process from running
l
l List files in long format (ls -l)
last Indicate last logins of users and ttys
launchctl Load or unload daemons/agents
ll List files in long format, showing invisible files (ls -la)
less Display output one screen at a time
let Evaluate expression •
lipo Convert a universal binary
ln Make links between files (hard links, symbolic links)
local Set a local (function) variable •
locate Find files
logname Print current login name
login log into the computer
logout Exit a login shell (bye) •
look Display lines beginning with a given string
lpr Print files
lprm Remove jobs from the print queue
lpstat Printer status information
ls List information about file(s)
lsregister Reset the Launch Services database
lsbom List a bill of materials file
lsof List open files
m
man Help manual
mdfind Spotlight search
mdutil Manage Spotlight metadata store
mkdir Create new folder(s)
mkfifo Make FIFOs (named pipes)
more Display output one screen at a time
mount Mount a file system
mv Move or rename files or directories
n
nano Simple text editor
net Manage network resources
netstat Show network status
networksetup Network and System Preferences
nice Set the priority of a command
nohup Run a command immune to hangups
ntfs.util NTFS file system utility
o
onintr Control the action of a shell interrupt
open Open a file/folder/URL/Application
opensnoop Snoop file opens as they occur
osacompile Compile Applescript
osascript Execute AppleScript
p
passwd Modify a user password
paste Merge lines of files
pbcopy Copy data to the clipboard
pbpaste Paste data from the Clipboard
ping Test a network connection
pkgutil Query and manipulate installed packages
plutil Property list utility
pmset Power Management settings
popd Restore the previous value of the current directory •
pr Convert text files for printing
printenv List environment variables
printf Format and print data •
ps Process status
pushd Save and then change the current directory
pwd Print Working Directory •
q
quota Display disk usage and limits
r
rcp Copy files between machines
read Read one line from standard input •
readonly Mark a variable or function as read-only •
reboot Stop and restart the system
return Exit a function •
rev Reverse lines of a file
rm Remove files
rmdir Remove folder(s)
rpm Remote Package Manager
rsync Remote file copy – Sync file tree (also RsyncX)
s
say Convert text to audible speech
screen Multiplex terminal, run remote shells via ssh
screencapture Capture screen image to file or disk
sdiff Merge two files interactively
security Administer Keychains, keys, certificates and the Security framework
sed Stream Editor
select Generate a list of items •
set Set a shell variable = value •
setfile Set attributes of HFS+ files
shift Shift positional parameters •
shopt Set shell options •
shutdown Shutdown or restart OS X
sips Scriptable image processing system
sleep Delay for a specified time
softwareupdate System software update tool
sort Sort text files
source Execute commands from a file •
split Split a file into fixed-size pieces
stop Stop a job or process
su Substitute user identity
sudo Execute a command as another user
sum Print a checksum for a file
suspend Suspend execution of this shell •
sw_vers Print Mac OS X operating system version
system_profiler Report system configuration
systemsetup Computer and display system settings
t
tail Output the last part of files
tar Tape ARchiver
tcpdump Dump traffic on a network
tee Redirect output to multiple files
test Condition evaluation •
textutil Manipulate text files in various formats (Doc,html,rtf)
time Measure Program Resource Use
times Print shell & shell process times •
top Display process information
touch Change file timestamps
tr Translate, squeeze, and/or delete characters
trap Execute a command when the shell receives a signal •
traceroute Trace Route to Host
true Do nothing, successfully
tty Print filename of terminal on stdin
type Describe a command •
u
ipconfig View and control IP configuration state
info Help info
install Copy files and set attributes
j
jobs List active jobs •
join Join lines on a common field
k
kextfind List kernel extensions
kickstart Configure Apple Remote Desktop
kill Stop a process from running
l
l List files in long format (ls -l)
last Indicate last logins of users and ttys
launchctl Load or unload daemons/agents
ll List files in long format, showing invisible files (ls -la)
less Display output one screen at a time
let Evaluate expression •
lipo Convert a universal binary
ln Make links between files (hard links, symbolic links)
local Set a local (function) variable •
locate Find files
logname Print current login name
login log into the computer
logout Exit a login shell (bye) •
look Display lines beginning with a given string
lpr Print files
lprm Remove jobs from the print queue
lpstat Printer status information
ls List information about file(s)
lsregister Reset the Launch Services database
lsbom List a bill of materials file
lsof List open files
m
man Help manual
mdfind Spotlight search
mdutil Manage Spotlight metadata store
mkdir Create new folder(s)
mkfifo Make FIFOs (named pipes)
more Display output one screen at a time
mount Mount a file system
mv Move or rename files or directories
n
nano Simple text editor
net Manage network resources
netstat Show network status
networksetup Network and System Preferences
nice Set the priority of a command
nohup Run a command immune to hangups
ntfs.util NTFS file system utility
o
onintr Control the action of a shell interrupt
open Open a file/folder/URL/Application
opensnoop Snoop file opens as they occur
osacompile Compile Applescript
osascript Execute AppleScript
p
passwd Modify a user password
paste Merge lines of files
pbcopy Copy data to the clipboard
pbpaste Paste data from the Clipboard
ping Test a network connection
pkgutil Query and manipulate installed packages
plutil Property list utility
pmset Power Management settings
popd Restore the previous value of the current directory •
pr Convert text files for printing
printenv List environment variables
printf Format and print data •
ps Process status
pushd Save and then change the current directory
pwd Print Working Directory •
q
quota Display disk usage and limits
r
rcp Copy files between machines
read Read one line from standard input •
readonly Mark a variable or function as read-only •
reboot Stop and restart the system
return Exit a function •
rev Reverse lines of a file
rm Remove files
rmdir Remove folder(s)
rpm Remote Package Manager
rsync Remote file copy – Sync file tree (also RsyncX)
s
say Convert text to audible speech
screen Multiplex terminal, run remote shells via ssh
screencapture Capture screen image to file or disk
sdiff Merge two files interactively
security Administer Keychains, keys, certificates and the Security framework
sed Stream Editor
select Generate a list of items •
set Set a shell variable = value •
setfile Set attributes of HFS+ files
shift Shift positional parameters •
shopt Set shell options •
shutdown Shutdown or restart OS X
sips Scriptable image processing system
sleep Delay for a specified time
softwareupdate System software update tool
sort Sort text files
source Execute commands from a file •
split Split a file into fixed-size pieces
stop Stop a job or process
su Substitute user identity
sudo Execute a command as another user
sum Print a checksum for a file
suspend Suspend execution of this shell •
sw_vers Print Mac OS X operating system version
system_profiler Report system configuration
systemsetup Computer and display system settings
t
tail Output the last part of files
tar Tape ARchiver
tcpdump Dump traffic on a network
tee Redirect output to multiple files
test Condition evaluation •
textutil Manipulate text files in various formats (Doc,html,rtf)
time Measure Program Resource Use
times Print shell & shell process times •
top Display process information
touch Change file timestamps
tr Translate, squeeze, and/or delete characters
trap Execute a command when the shell receives a signal •
traceroute Trace Route to Host
true Do nothing, successfully
tty Print filename of terminal on stdin
type Describe a command •
u
ufs.util Mount/unmount UFS file system
ulimit limit the use of system-wide resources •
umask Users file creation mask
umount Unmount a device
unalias Remove an alias •
uname Print system information
unexpand Convert spaces to tabs
uniq Uniquify files
units Convert units from one scale to another
unset Remove variable or function names •
until Loop command •
uptime Show how long system has been running
users Print login names of users currently logged in
uuencode Encode a binary file
uudecode Decode a file created by uuencode
uuidgen Generate a Unique ID (UUID/GUID)
uucp Unix to Unix copy
v
vi Text Editor
w
wait Wait for a process to complete •
wc Print byte, word, and line counts
whatis Search the whatis database for complete words
where Report all known instances of a command
which Locate a program file in the user’s path
while Loop command •
who Print all usernames currently logged on
whoami Print the current user id and name (`id -un’)
write Send a message to another user
x
xargs Execute utility – passing arguments
yes Print a string until interrupted
!! Run the last command again
ulimit limit the use of system-wide resources •
umask Users file creation mask
umount Unmount a device
unalias Remove an alias •
uname Print system information
unexpand Convert spaces to tabs
uniq Uniquify files
units Convert units from one scale to another
unset Remove variable or function names •
until Loop command •
uptime Show how long system has been running
users Print login names of users currently logged in
uuencode Encode a binary file
uudecode Decode a file created by uuencode
uuidgen Generate a Unique ID (UUID/GUID)
uucp Unix to Unix copy
v
vi Text Editor
w
wait Wait for a process to complete •
wc Print byte, word, and line counts
whatis Search the whatis database for complete words
where Report all known instances of a command
which Locate a program file in the user’s path
while Loop command •
who Print all usernames currently logged on
whoami Print the current user id and name (`id -un’)
write Send a message to another user
x
xargs Execute utility – passing arguments
yes Print a string until interrupted
!! Run the last command again
Como les dije antes, el saber NO ocupa lugar y piensen que en realidad todo pasa por aquí, lo que vemos en nuestra Mac es la interfaz gráfica que se comunica con esto en nuestro Sistema Operativo.
Hay mucho trucos que se pueden hacer “como bloquear nuestras conexiones salientes” para que nuestro software “gratias” para probar no se comunique con el desarrollador del mismo y algunos pueden hacer que nuestra Mac salga de un problema.
Mas adelante trataremos de ir posteando estos trucos.
Fuente:
http://foro-mac.com.ar/tutorial-como-usar-la-terminal-en-mac/
Mas adelante trataremos de ir posteando estos trucos.
Fuente:
http://foro-mac.com.ar/tutorial-como-usar-la-terminal-en-mac/
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario